central-limit-theorem
说明: 将中心极限定理应用于不同概率分布的PDF和CDF的MATLAB项目。
(A MATLAB project which applies the central limit theorem on PDFs and CDFs of different probability distributions.)
(A MATLAB project which applies the central limit theorem on PDFs and CDFs of different probability distributions.)
文件列表:
Figures (0, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q2 (0, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q2\q2_1.jpg (77958, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q2\q2_2.jpg (60735, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q2\q2_3.jpg (45641, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q3 (0, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q3\q3_1.jpg (72944, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q3\q3_2.jpg (58094, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q3\q3_3.jpg (45966, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q4 (0, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q4\q4_1.jpg (59707, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q4\q4_2.jpg (41685, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q4\q4_3.jpg (39134, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q5 (0, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q5\q5_1.jpg (66327, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q5\q5_2.jpg (53808, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q5\q5_3.jpg (56010, 2022-08-08)
LICENSE (1071, 2022-08-08)
Proof (0, 2022-08-08)
Proof\Q1 (0, 2022-08-08)
Proof\Q1\q1.jpg (59867, 2022-08-08)
hw_desc.pdf (112262, 2022-08-08)
hw_report.pdf (496032, 2022-08-08)
main.m (10149, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q2 (0, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q2\q2_1.jpg (77958, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q2\q2_2.jpg (60735, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q2\q2_3.jpg (45641, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q3 (0, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q3\q3_1.jpg (72944, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q3\q3_2.jpg (58094, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q3\q3_3.jpg (45966, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q4 (0, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q4\q4_1.jpg (59707, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q4\q4_2.jpg (41685, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q4\q4_3.jpg (39134, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q5 (0, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q5\q5_1.jpg (66327, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q5\q5_2.jpg (53808, 2022-08-08)
Figures\Q5\q5_3.jpg (56010, 2022-08-08)
LICENSE (1071, 2022-08-08)
Proof (0, 2022-08-08)
Proof\Q1 (0, 2022-08-08)
Proof\Q1\q1.jpg (59867, 2022-08-08)
hw_desc.pdf (112262, 2022-08-08)
hw_report.pdf (496032, 2022-08-08)
main.m (10149, 2022-08-08)
# central-limit-theorem
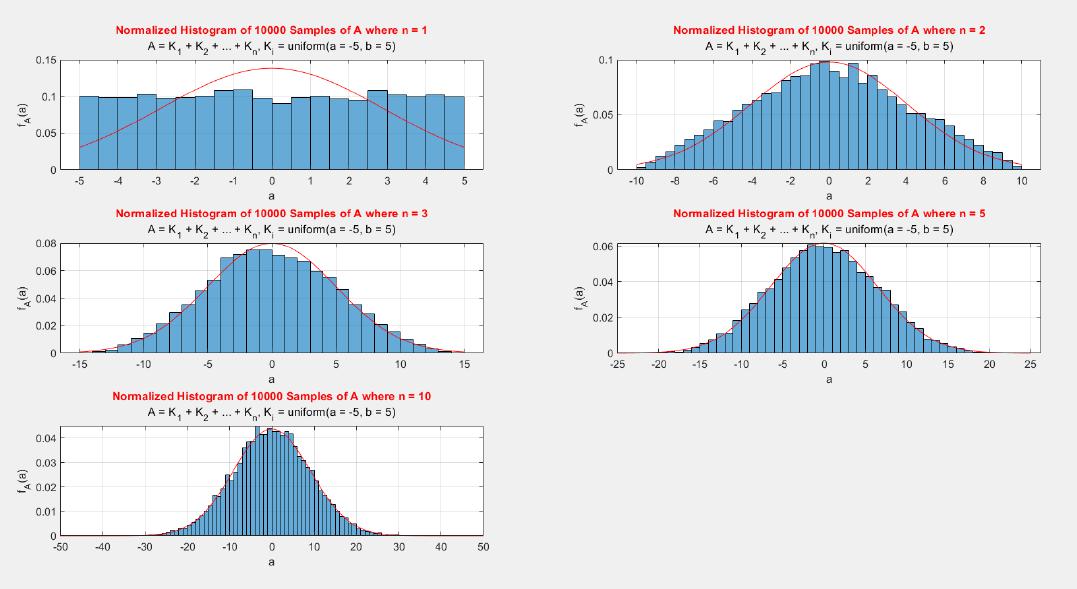
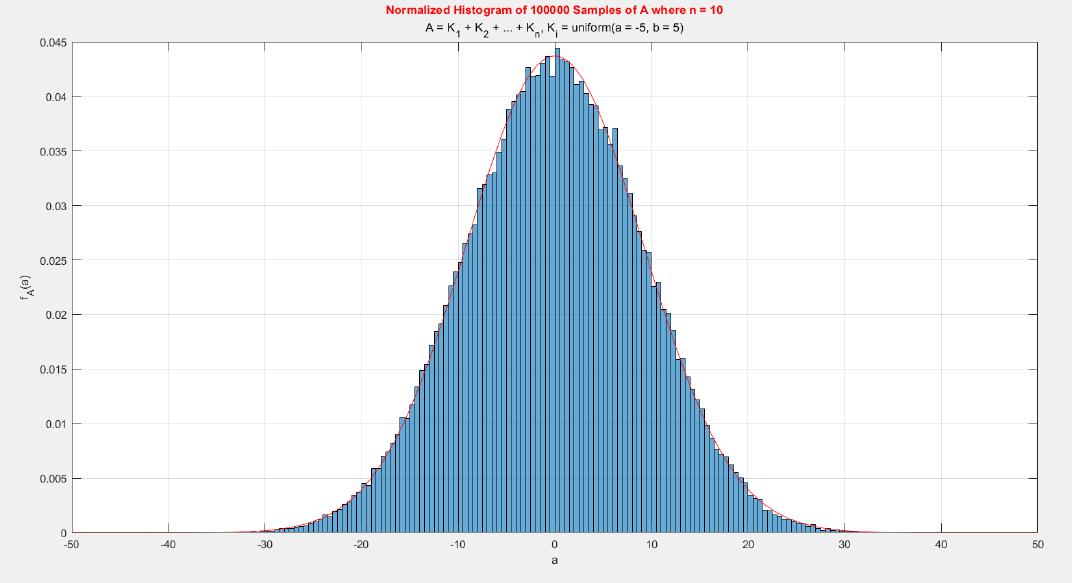
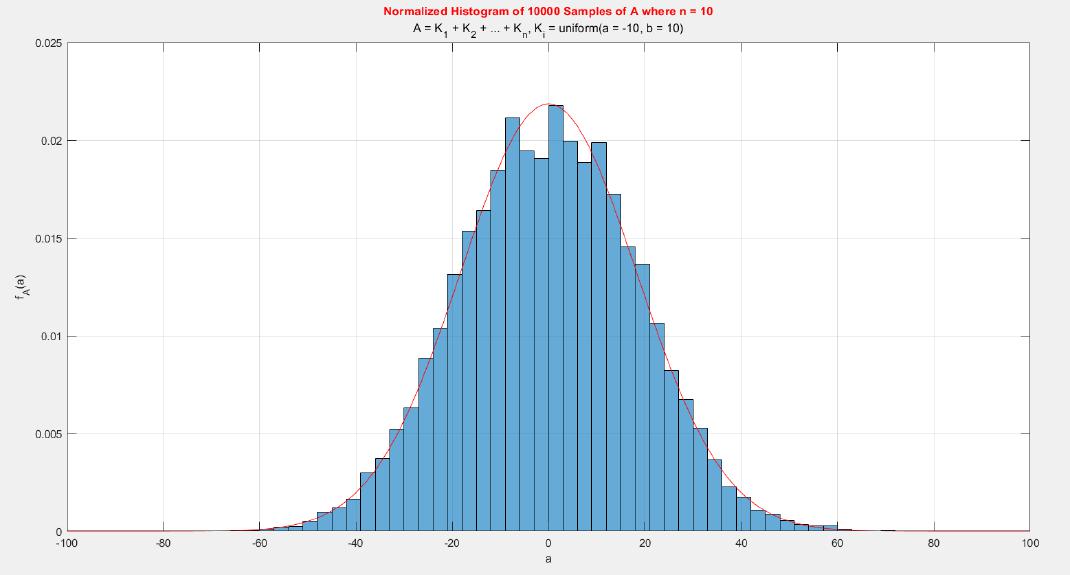
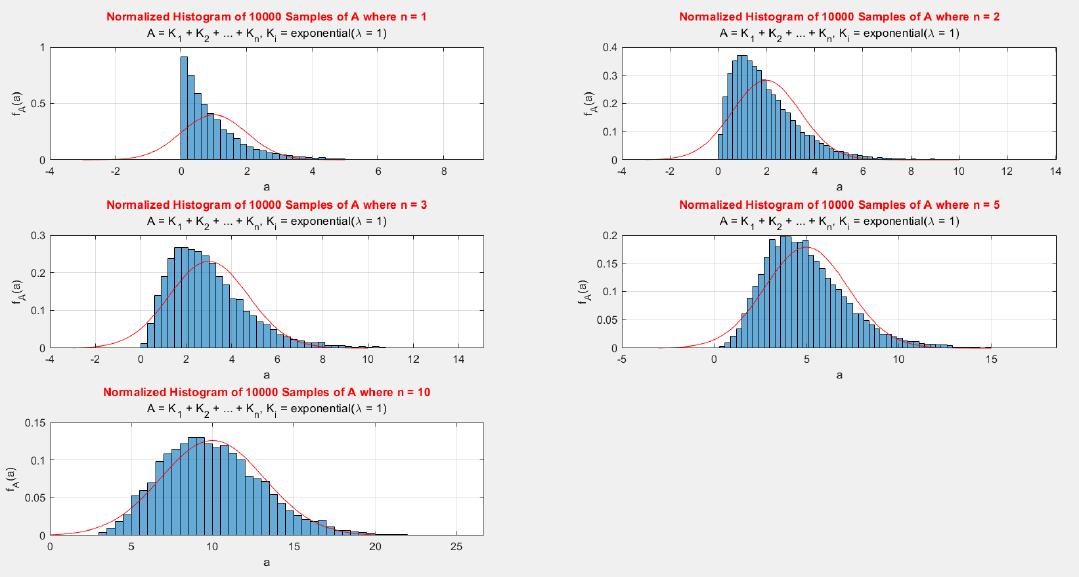
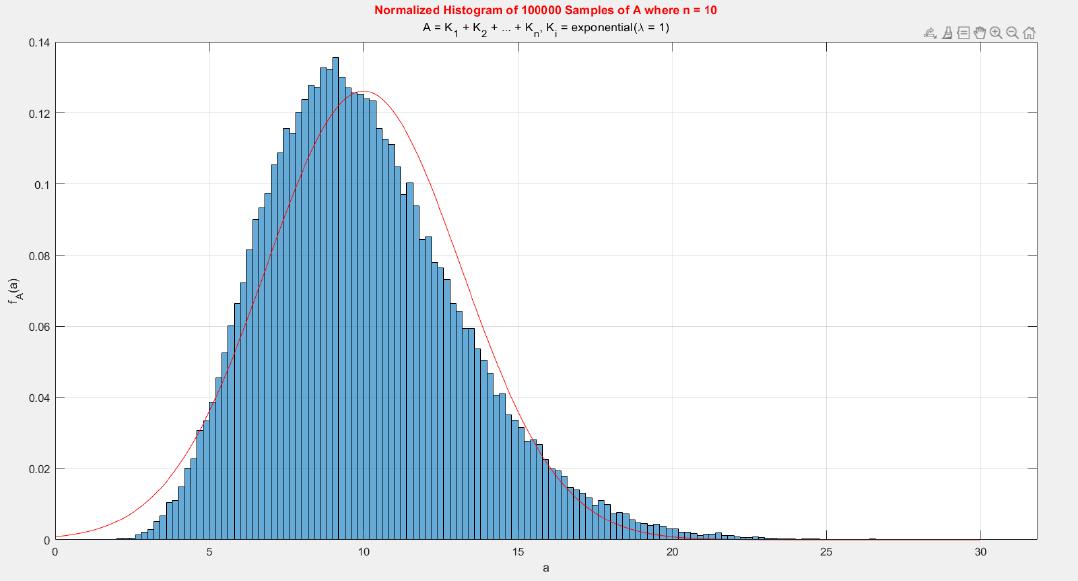
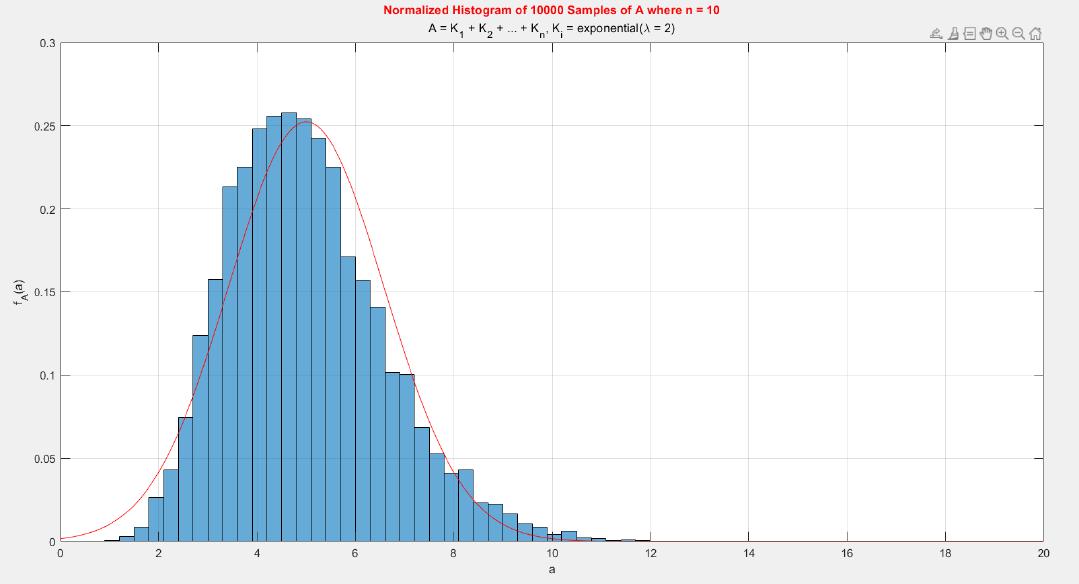
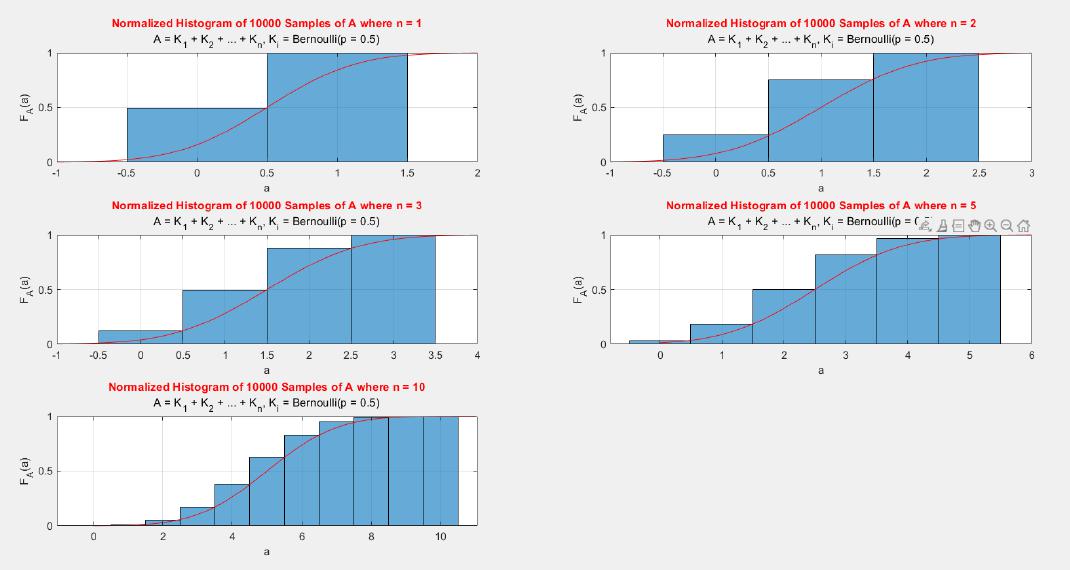
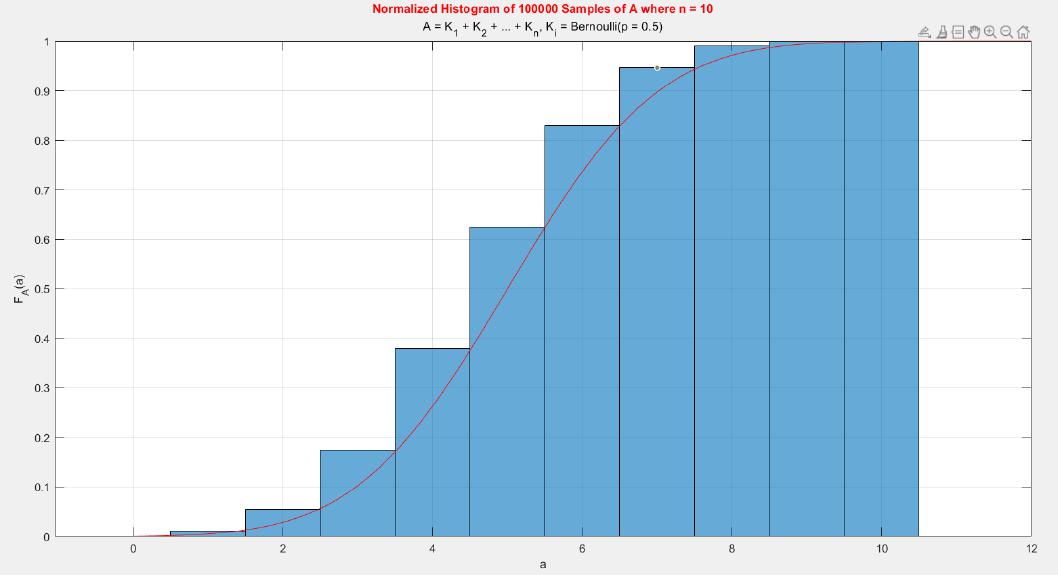
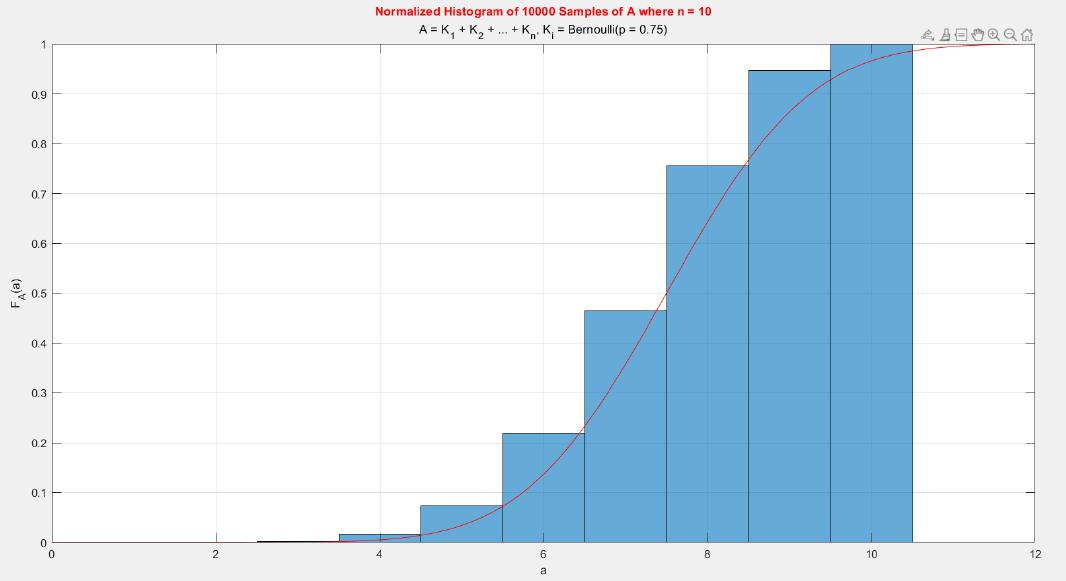
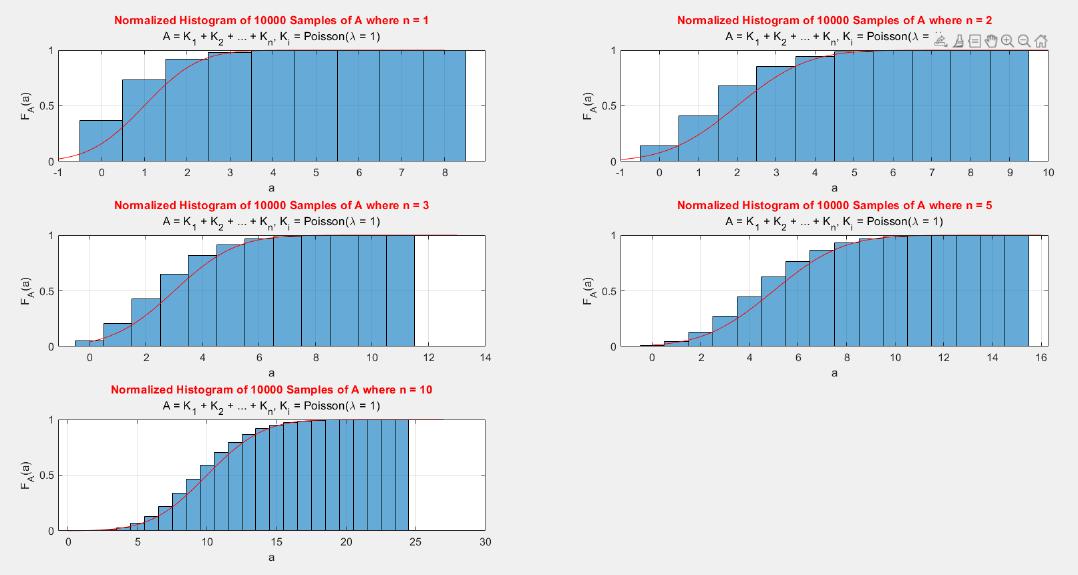
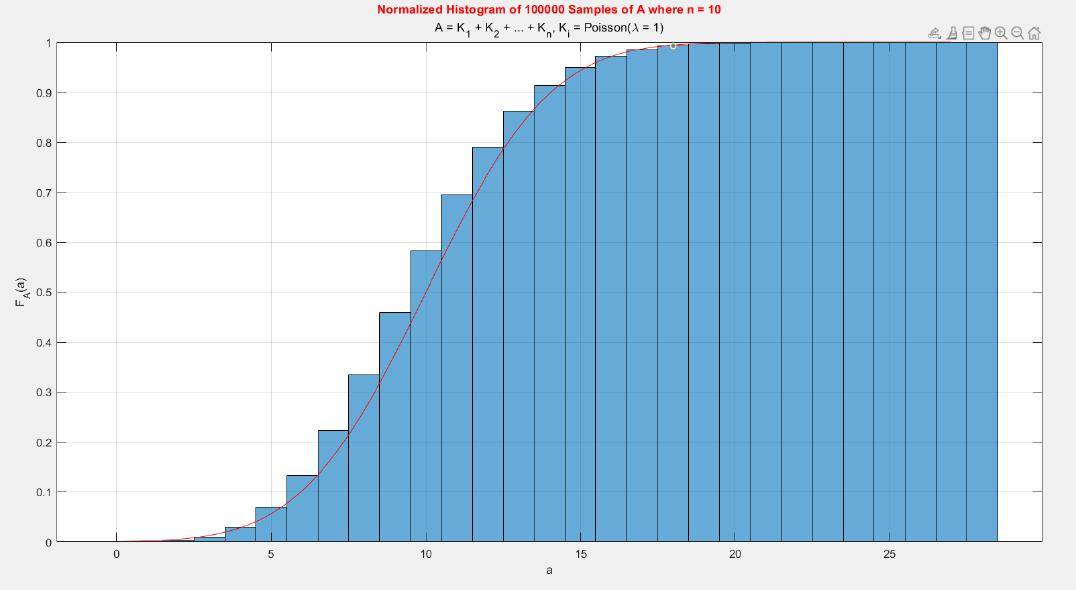
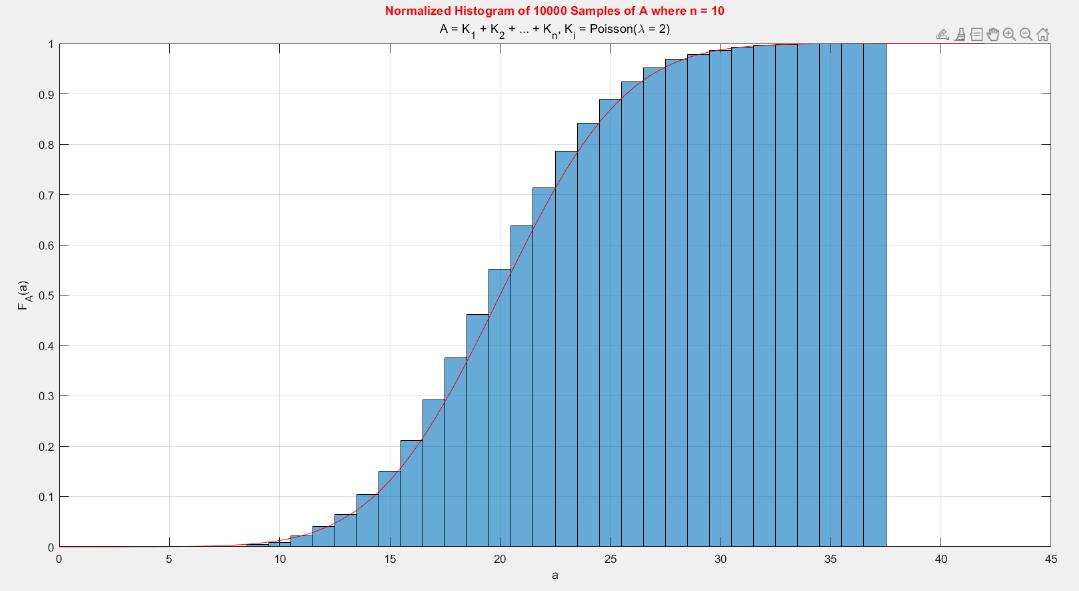
A MATLAB project which applies the central limit theorem (CLT) on probability density functions (PDFs) and cumulative distribution functions (CDFs) of different probability distributions such as uniform, exponential, Bernoulli, and Poisson distribution.
The central limit theorem (CLT) implies that given , a sequence of independent and identically distributed (IID) random variables with expected value  and variance , the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of  has the property =\Phi(z)). Briefly, the theorem states that as n increases, the sum of n IID random variables converges to a [normal distribution](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Normal_distribution).
This homework was assigned for the Probability for Electrical Engineers (EE 313) course in the Fall 2021-22 semester.
## Run on Terminal
```sh
matlab -nodisplay -nosplash -nodesktop -r "run('main.m');exit;"
```
## Proof
### 1) E[A] and Var[A]
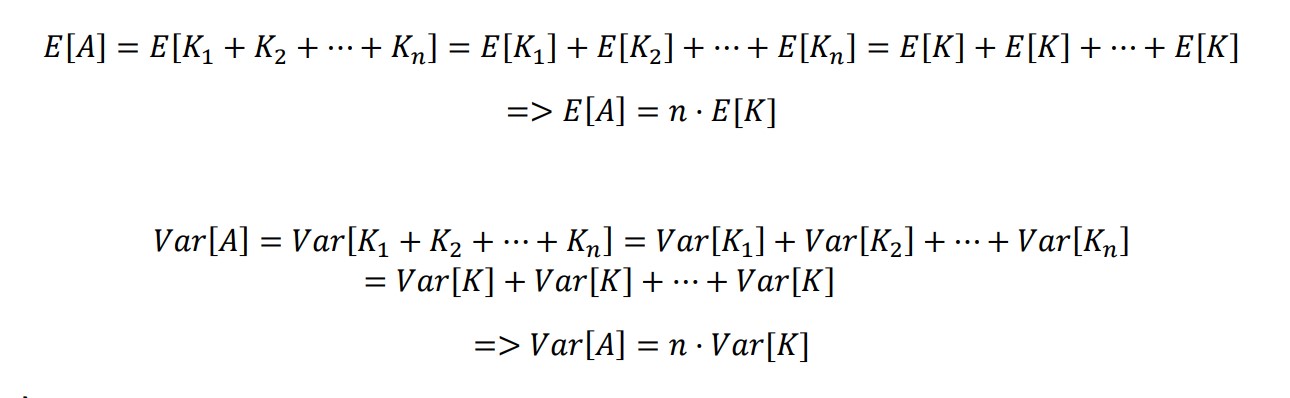
近期下载者:
相关文件:
收藏者: