TDN
说明: 可信分布式网络。(也是构建去中心化应用程序的微观框架)
(TDN,Trusted Distributed Network. (Also a micro-framework for building decentralized applications))
(TDN,Trusted Distributed Network. (Also a micro-framework for building decentralized applications))
文件列表:
Cargo.toml (251, 2023-05-28)
LICENSE-APACHE (11356, 2023-05-28)
LICENSE-MIT (1066, 2023-05-28)
did (0, 2023-05-28)
did\Cargo.toml (1220, 2023-05-28)
did\src (0, 2023-05-28)
did\src\bip32.rs (10618, 2023-05-28)
did\src\bip39.rs (23773, 2023-05-28)
did\src\bip44.rs (2712, 2023-05-28)
did\src\error.rs (1857, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language.rs (8592, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language (0, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\chinese_simplified.rs (14885, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\chinese_traditional.rs (14885, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\czech.rs (22050, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\english.rs (20141, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\french.rs (31150, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\italian.rs (30406, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\japanese.rs (40796, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\korean.rs (52205, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\portuguese.rs (22816, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\spanish.rs (28369, 2023-05-28)
did\src\lib.rs (2522, 2023-05-28)
storage (0, 2023-05-28)
storage\Cargo.toml (852, 2023-05-28)
storage\src (0, 2023-05-28)
storage\src\decentralized.rs (0, 2023-05-28)
storage\src\distributed.rs (3819, 2023-05-28)
storage\src\file.rs (2163, 2023-05-28)
storage\src\lib.rs (168, 2023-05-28)
storage\src\local.rs (4840, 2023-05-28)
... ...
LICENSE-APACHE (11356, 2023-05-28)
LICENSE-MIT (1066, 2023-05-28)
did (0, 2023-05-28)
did\Cargo.toml (1220, 2023-05-28)
did\src (0, 2023-05-28)
did\src\bip32.rs (10618, 2023-05-28)
did\src\bip39.rs (23773, 2023-05-28)
did\src\bip44.rs (2712, 2023-05-28)
did\src\error.rs (1857, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language.rs (8592, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language (0, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\chinese_simplified.rs (14885, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\chinese_traditional.rs (14885, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\czech.rs (22050, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\english.rs (20141, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\french.rs (31150, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\italian.rs (30406, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\japanese.rs (40796, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\korean.rs (52205, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\portuguese.rs (22816, 2023-05-28)
did\src\language\spanish.rs (28369, 2023-05-28)
did\src\lib.rs (2522, 2023-05-28)
storage (0, 2023-05-28)
storage\Cargo.toml (852, 2023-05-28)
storage\src (0, 2023-05-28)
storage\src\decentralized.rs (0, 2023-05-28)
storage\src\distributed.rs (3819, 2023-05-28)
storage\src\file.rs (2163, 2023-05-28)
storage\src\lib.rs (168, 2023-05-28)
storage\src\local.rs (4840, 2023-05-28)
... ...
[](https://crates.io/crates/tdn) [](https://docs.rs/tdn)
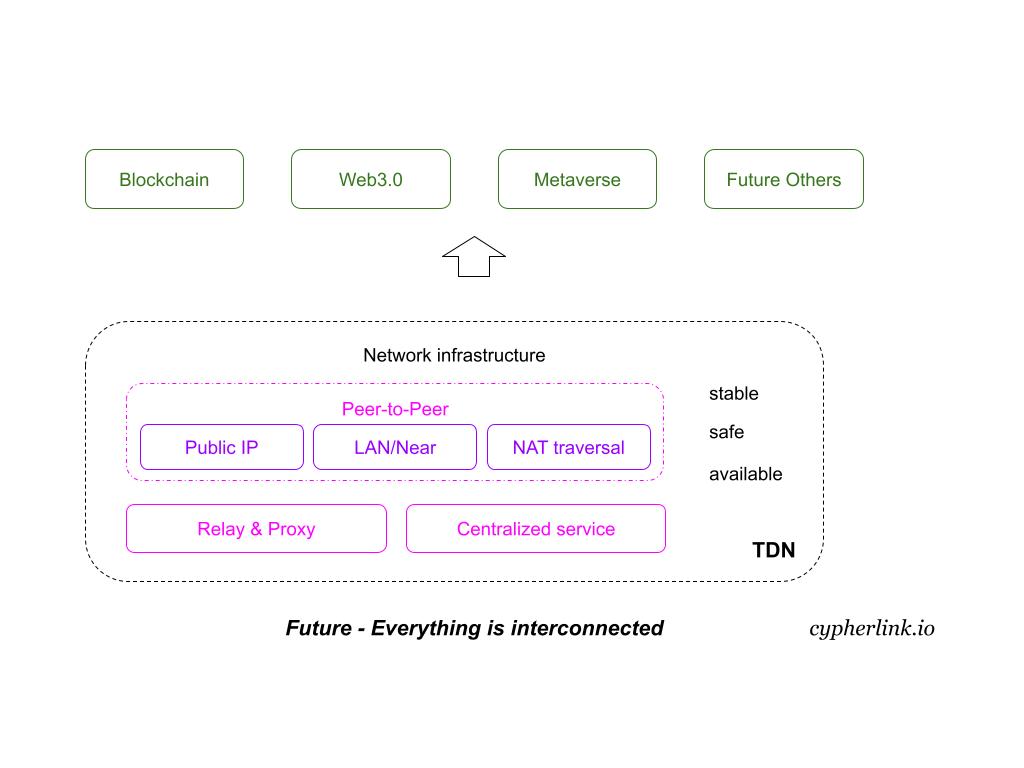
*TDN: Let data transfer safely, make the network stable, secure, and highly available.*
As the network interconnection, TDN includes peer-to-peer, centralized gateway, proxy & relay service, LAN, RPC, Near, etc.
As the framework of decentralized applications, TDN uses the `Layer` and `Group` models. We built this framework because we feel that the blockchain is very limited. If you want a more open and free distributed application development technology, and Pluggable, lightweight application framework, TDN can satisfy you.
## Example
```
use std::sync::Arc;
use tdn::prelude::*;
use tdn::types::rpc::{json, RpcError, RpcHandler, RpcParam};
struct State(u32);
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() {
let (peer_addr, send, mut out_recv) = start().await.unwrap();
println!("Example: peer id: {:?}", peer_addr);
let mut rpc_handler = RpcHandler::new(State(1));
rpc_handler.add_method("say_hello", |_params: Vec, state: Arc| async move {
assert_eq!(1, state.0);
Ok(HandleResult::rpc(json!("hello")))
});
while let Some(message) = out_recv.recv().await {
match message {
ReceiveMessage::Own(msg) => match msg {
RecvType::Connect(peer, _data) => {
println!("receive own peer {} join", peer.id.short_show());
}
RecvType::Leave(peer) => {
println!("receive own peer {} leave", peer.id.short_show());
}
RecvType::Event(peer_id, _data) => {
println!("receive own event from {}", peer_id.short_show());
}
_ => {
println!("nerver here!")
}
},
ReceiveMessage::Group(msg) => match msg {
RecvType::Connect(peer, _data) => {
println!("receive group peer {} join", peer.id.short_show());
}
RecvType::Result(..) => {
//
}
RecvType::Leave(peer) => {
println!("receive group peer {} leave", peer.id.short_show());
}
RecvType::Event(peer_id, _data) => {
println!("receive group event from {}", peer_id.short_show());
}
_ => {}
},
ReceiveMessage::Layer(fgid, _tgid, msg) => match msg {
RecvType::Connect(peer, _data) => {
println!("Layer Join: {}, Addr: {}.", fgid, peer.id.short_show());
}
RecvType::Result(..) => {
//
}
_ => {}
},
ReceiveMessage::Rpc(uid, params, is_ws) => {
if let Ok(HandleResult {
mut rpcs,
owns: _,
groups: _,
layers: _,
networks: _,
}) = rpc_handler.handle(params).await
{
loop {
if rpcs.len() != 0 {
let msg = rpcs.remove(0);
send.send(SendMessage::Rpc(uid, msg, is_ws))
.await
.expect("TDN channel closed");
} else {
break;
}
}
}
}
ReceiveMessage::NetworkLost => {
println!("No network connections");
}
}
}
}
```
- install `lastest` Rust and `cd ./tdn`
- `cargo run --example simple` Congratulation, you are running a trusted distributed network :)
[more sample](./tdn/examples)
## Features
- Support different data structures
- Support different consensus algorithms
- Support different permission mechanisms
- Support different account systems
- Applications can communicate with others
- Trust can be passed on and accumulated
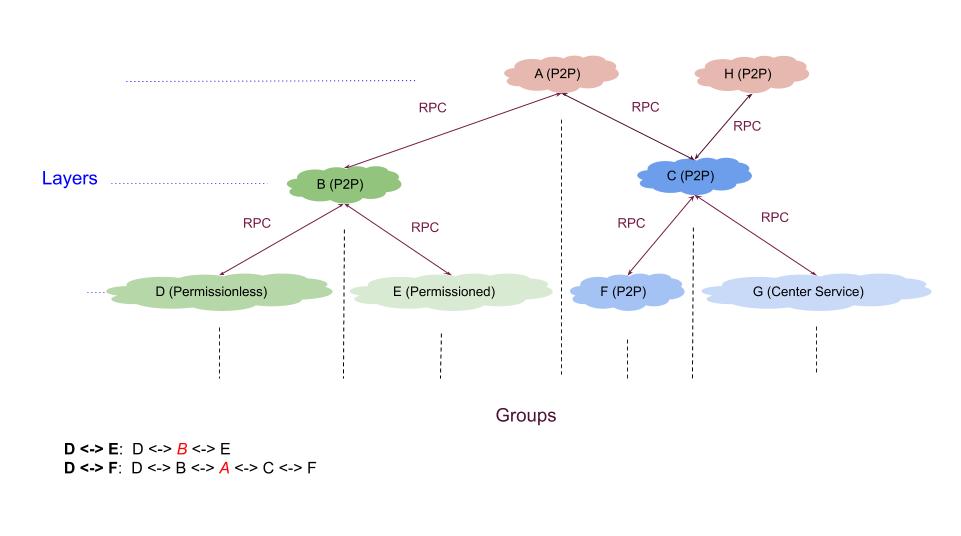
## 4-type Applications
TDN can build 4-type network for applications.
Use `feature` to control. (Tip: one group, is one chain, is one application)
- **single**. Support only one group, and no layers. Like `Bitcoin`.
- **std** (default). Support only one group, and multiple layers (cross-chain, Interactive with other groups).
- **multiple**. Support many groups (in one runtime, support many applications), and no layers. Like `Ethereum`.
- **full**. Support many groups, and multiple layers.
## Architecture
## Pluggable library
- [tdn-did](./did) decentralized identity.
- [tdn-storage](./storage) Storage library, include Local file, Local db, Distributed db, Decentralized db.
- [tdn-permission](https://github.com/cympletech/tdn-permission) Group permission library, include permissioned & permissionless group algorithm.
## For more information, please visit:
- Website: https://cympletech.com
- Twitter: https://twitter.com/cympletech
- Discord: https://discord.gg/UfFjp6Kaj4
- E-mail: contact@cympletech.com
### Core QA
1. **What is Layers & Groups?**
Simply `Group` is application, one application is one group, `Layer` is communication between apps. In the Group, users can define everything. The Layer is divided into upper and lower, upper is this application depends on others, lower is others depends on this. If app is an independent application that does not interact with other applications, then you can completely ignore Layer.
2. **Different consensus?**
Consensus is expensive. Not all applications require global consensus to be used. Local consensus can speed up the usability of applications. Local consensus can be different. Users can define self-consensus in different applications. The results of the consensus can also be sent to different applications through the layer. In this way, the consensus results can be passed to the upper layer. After the upper layer consensus is obtained, a larger range and stronger consensus irreversible result can be formed.
3. **Different permission?**
Why do we need a different permission mechanism? Because in different applications, some applications require an open permissionless environment, such as Bitcoin, and some require a permissioned environment. For example, We built a synchronization which is distributed between my own devices is inaccessible to outsiders. At the same time, `Layer` supports applications in different permission environments, allowing data interaction.
4. **Different block & transaction data structure?**
Similarly, different applications have completely different data structures. Therefore, in the TDN, we use a common byte stream format. Users can customize the data format of the application. The communication with the TDN is only serialization and deserialization.
5. **Different account system?**
In the TDN, there will be a default p2p network address (PeerId) in the p2p system. The user can use the PeerId to replace the ip address. The TDN will search the PeerId in the network and establish a connection. At the same time, the user can also Fully customize the account model and connection verification method of the application.
## License
This project is licensed under either of
* Apache License, Version 2.0, ([LICENSE-APACHE](LICENSE-APACHE) or
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0)
* MIT license ([LICENSE-MIT](LICENSE-MIT) or
http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
at your option.
近期下载者:
相关文件:
收藏者:
