tutorials
所属分类:文章/文档
开发工具:Shell
文件大小:0KB
下载次数:0
上传日期:2023-08-03 06:19:10
上 传 者:
sh-1993
说明: 图603:以编程方式遍历链接的数据,
(FIWARE 603: Traversing Linked Data Programmatically,)
文件列表:
.env (391, 2023-12-04)
FIWARE Working with Linked Data.postman_collection.json (38242, 2023-12-04)
LICENSE (1085, 2023-12-04)
docker-compose/ (0, 2023-12-04)
docker-compose/common.yml (3311, 2023-12-04)
docker-compose/orion-ld.yml (2026, 2023-12-04)
docker-compose/scorpio.yml (2227, 2023-12-04)
docker-compose/stellio.yml (4739, 2023-12-04)
docker-compose/stellio/ (0, 2023-12-04)
docker-compose/stellio/kafka/ (0, 2023-12-04)
docker-compose/stellio/kafka/update_run.sh (486, 2023-12-04)
import-data (24755, 2023-12-04)
services (7667, 2023-12-04)
[](https://www.fiware.org/developers)
[](https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_gs/CIM/001_099/009/01.07.01_60/gs_cim009v010701p.pdf)
[](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/core/README.md)
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
[](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fiware)
[](https://w3c.github.io/json-ld-syntax/)
[](https://fiware-tutorials.rtfd.io)
This tutorial teaches FIWARE users how to architect and design a system based on **linked data** and to alter linked
data context programmatically. The tutorial extends the knowledge gained from the equivalent
[NGSI-v2 tutorial](https://github.com/FIWARE/tutorials.Accessing-Context/) and enables a user understand how to write
code in an [NGSI-LD](https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_gs/CIM/001_099/009/01.07.01_60/gs_cim009v010701p.pdf) capable
[Node.js](https://nodejs.org/) [Express](https://expressjs.com/) application in order to retrieve and alter context
data. This removes the need to use the command-line to invoke cUrl commands.
The tutorial is mainly concerned with discussing code written in Node.js, however some of the results can be checked by
making [cUrl](https://ec.haxx.se/) commands.
[Postman documentation](https://fiware.github.io/tutorials.Working-with-Linked-Data) for the same commands is also
available.
[](https://app.getpostman.com/run-collection/644a1df1e2d226da65ef)
[](https://gitpod.io/#https://github.com/FIWARE/tutorials.Working-with-Linked-Data/tree/NGSI-v2)
- このチュートリアルは[日本語](README.ja.md)でもご覧いただけます。
:warning: **Note:** This tutorial is designed for **NGSI-v2** developers looking to switch or upgrade systems to
**NGSI-LD**, if you are building a linked data system from scratch or you are not already familiar with **NGSI-v2** then
it is recommmended that you look directly at the
[NGSI-LD developers tutorial](https://ngsi-ld-tutorials.readthedocs.io/) documentation.
## Contents
Details
- [Working with Linked Data Entities](#working-with-linked-data-entities)
- [Linked Data Entities within a stock management system](#linked-data-entities-within-a-stock-management-system)
- [The teaching goal of this tutorial](#the-teaching-goal-of-this-tutorial)
- [Stock Management Frontend](#stock-management-frontend)
- [Prerequisites](#prerequisites)
- [Docker](#docker)
- [Cygwin](#cygwin)
- [Architecture](#architecture)
- [Start Up](#start-up)
- [Traversing Linked Data Programmatically](#traversing-linked-data-programmatically)
- [Reading Linked Data](#reading-linked-data)
- [Initializing the library](#initializing-the-library)
- [Retrieve a known Store](#retrieve-a-known-store)
- [Aggregating and Traversing Linked Data](#aggregating-and-traversing-linked-data)
- [Find Shelves within a known Store](#find-shelves-within-a-known-store)
- [Retrieve Stocked Products from shelves](#retrieve-stocked-products-from-shelves)
- [Retrieve Product Details for selected shelves](#retrieve-product-details-for-selected-shelves)
- [Updating Linked Data](#updating-linked-data)
- [Find a shelf stocking a product](#find-a-shelf-stocking-a-product)
- [Update the state of a shelf](#update-the-state-of-a-shelf)
- [Interoperability using Linked Data](#interoperability-using-linked-data)
- [Creating an Entity using an Alternate Schema](#creating-an-entity-using-an-alternate-schema)
- [Reading an Entity using the default schema](#reading-an-entity-using-the-default-schema)
- [Reading an Entity using an alternate schema](#reading-an-entity-using-an-alternate-schema)
- [Applying Entity Expansion/Compaction](#applying-entity-expansioncompaction)
# Working with Linked Data Entities
> - “This is the house that Jack built.
> - This is the malt that lay in the house that Jack built.
> - This is the rat that ate the malt
That lay in the house that Jack built.
> - This is the cat
That killed the rat that ate the malt
That lay in the house that Jack built.
> - This is the dog that chased the cat
That killed the rat that ate the malt
That lay in the house that
> Jack built.”
>
> ― This Is the House That Jack Built, Traditional English Nursery Rhyme
NGSI-LD is an evolution of NGSI-v2, so it should not be surprising that Smart solutions based on NGSI-LD will need to
cover the same basic scenarios as outlined in the previous NGSI-v2
[tutorial](https://github.com/FIWARE/tutorials.Accessing-Context/) on programmatic data access.
NGSI-LD Linked data formalizes the structure of context entities to a greater degree, through restricting data
attributes to be defined as either _Property_ attributes or _Relationship_ attributes only. This means that it is
possible to traverse the context data graph with greater certainty when moving from one _Relationship_ to another. All
the context data entities within the system are defined by JSON-LD data models, which are formally defined by
referencing a context file, and this programmatic definition should guarantee that the associated linked entity exists.
Three basic data access scenarios for the supermarket are defined below:
- Reading Data - e.g. Give me all the data for the **Building** entity `urn:ngsi-ld:Building:store001`
- Aggregation - e.g. Combine the **Products** entities sold in **Building** `urn:ngsi-ld:Building:store001` and
display the goods for sale
- Altering context within the system - e.g. Make a sale of a product:
- Update the daily sales records by the price of the **Product**
- decrement the `numberOfItems` of the **Shelf** entity
- Create a new Transaction Log record showing the sale has occurred
- Raise an alert in the warehouse if less than 10 objects remain on sale
- etc.
Further advanced scenarios will be covered in later tutorials
## Linked Data Entities within a stock management system
The supermarket data created in the [previous tutorial](https://github.com/FIWARE/tutorials.Relationships-Linked-Data/)
will be loaded into the context broker. The existing relationships between the entities are defined as shown below:
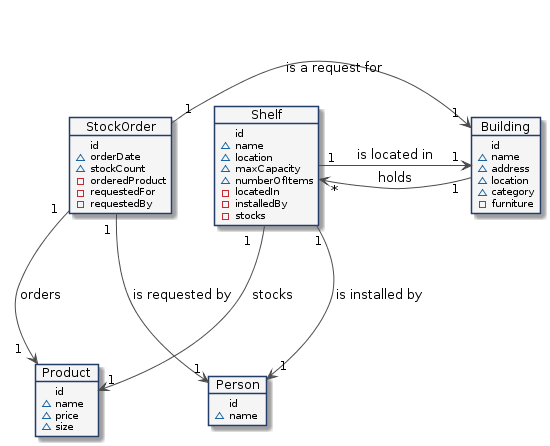
The **Building**, **Product**, **Shelf** and **StockOrder** entities will be used to display data on the frontend of our
demo application.
## The teaching goal of this tutorial
The aim of this tutorial is to improve developer understanding of programmatic access of context data through defining
and discussing a series of generic code examples covering common data access scenarios. For this purpose a simple
Node.js Express application will be created.
The intention here is not to teach users how to write an application in Express - indeed any language could have been
chosen. It is merely to show how **any** sample programming language could be used alter the context to achieve the
business logic goals.
Obviously, your choice of programming language will depend upon your own business needs - when reading the code below
please keep this in mind and substitute Node.js with your own programming language as appropriate.
# Stock Management Frontend
All the code Node.js Express for the demo can be found within the `ngsi-ld` folder within the GitHub repository.
[Stock Management example](https://github.com/FIWARE/tutorials.Step-by-Step/tree/master/context-provider). The
application runs on the following URLs:
- `http://localhost:3000/app/store/urn:ngsi-ld:Building:store001`
- `http://localhost:3000/app/store/urn:ngsi-ld:Building:store002`
- `http://localhost:3000/app/store/urn:ngsi-ld:Building:store003`
- `http://localhost:3000/app/store/urn:ngsi-ld:Building:store004`
> :information_source: **Tip** Additionally, you can also watch the status of recent requests yourself by following the
> container logs or viewing information on `localhost:3000/app/monitor` on a web browser.
>
> 
# Prerequisites
## Docker
To keep things simple all components will be run using [Docker](https://www.docker.com). **Docker** is a container
technology which allows to different components isolated into their respective environments.
- To install Docker on Windows follow the instructions [here](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/)
- To install Docker on Mac follow the instructions [here](https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-mac/)
- To install Docker on Linux follow the instructions [here](https://docs.docker.com/install/)
**Docker Compose** is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications. A
[YAML file](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/fiware/tutorials.Working-with-Linked-Data/master/docker-compose/orion-ld.yml)
is used configure the required services for the application. This means all container services can be brought up in a
single command. Docker Compose is installed by default as part of Docker for Windows and Docker for Mac, however Linux
users will need to follow the instructions found [here](https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/)
## Cygwin
We will start up our services using a simple bash script. Windows users should download [cygwin](http://www.cygwin.com/)
to provide a command-line functionality similar to a Linux distribution on Windows.
# Architecture
The demo Supermarket application will send and receive NGSI-LD calls to a compliant context broker. Since the NGSI-LD
interface is available on an experimental version of the
[Orion Context Broker](https://fiware-orion.readthedocs.io/en/latest/), the demo application will only make use of one
FIWARE component.
Currently, the Orion Context Broker relies on open source [MongoDB](https://www.mongodb.com/) technology to keep
persistence of the context data it holds. To request context data from external sources, a simple Context Provider NGSI
proxy has also been added. To visualize and interact with the Context we will add a simple Express application
Therefore, the architecture will consist of three elements:
- The [Orion Context Broker](https://fiware-orion.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) which will receive requests using
[NGSI-LD](https://forge.etsi.org/swagger/ui/?url=https://forge.etsi.org/rep/NGSI-LD/NGSI-LD/raw/master/spec/updated/generated/full_api.json)
- The underlying [MongoDB](https://www.mongodb.com/) database :
- Used by the Orion Context Broker to hold context data information such as data entities, subscriptions and
registrations
- The **Stock Management Frontend** which will:
- Display store information
- Show which products can be bought at each store
- Allow users to "buy" products and reduce the stock count.
Since all interactions between the elements are initiated by HTTP requests, the entities can be containerized and run
from exposed ports.
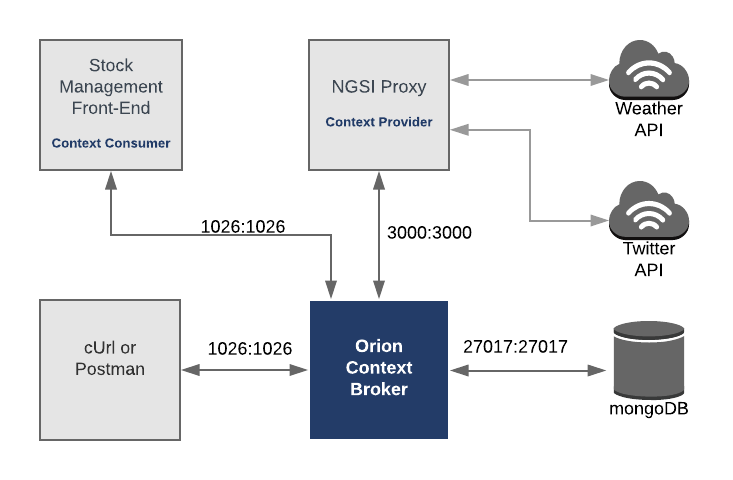
The necessary configuration information for the **Context Provider NGSI proxy** can be seen in the services section the
of the associated `orion-ld.yml` file:
```yaml
tutorial:
image: quay.io/fiware/tutorials.context-provider
hostname: context-provider
container_name: fiware-tutorial
networks:
- default
expose:
- '3000'
ports:
- '3000:3000'
environment:
- 'DEBUG=tutorial:*'
- 'WEB_APP_PORT=3000'
- 'NGSI_VERSION=ngsi-ld'
- 'CONTEXT_BROKER=http://orion:1026/ngsi-ld/v1'
```
The `tutorial` container is driven by environment variables as shown:
| Key | Value | Description |
| -------------- | ------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| DEBUG | `tutorial:*` | Debug flag used for logging |
| WEB_APP_PORT | `3000` | Port used by the Context Provider NGSI proxy and web-app for viewing data |
| CONTEXT_BROKER | `http://orion:1026/ngsi-ld/v1` | URL of the context broker to connect to update context |
The other `tutorial` container configuration values described in the YAML file are not used in this section of the
tutorial.
The configuration information for MongoDB and the Orion Context Broker has been described in a
[previous tutorial](https://github.com/FIWARE/tutorials.Relationships-Linked-Data/)
# Start Up
All services can be initialised from the command-line by running the
[services](https://github.com/FIWARE/tutorials.Relationships-Linked-Data/blob/NGSI-v2/services) Bash script provided
within the repository. Please clone the repository and create the necessary images by running the commands as shown:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/FIWARE/tutorials.Working-with-Linked-Data.git
cd tutorials.Working-with-Linked-Data
git checkout NGSI-v2
./services orion
```
> **Note:** If you want to clean up and start over again you can do so with the following command:
>
> ```
> ./services stop
> ```
---
# Traversing Linked Data Programmatically
Goto `http://localhost:3000/app/store/urn:ngsi-ld:Building:store001` to display and interact with the working
Supermarket data application.
## Reading Linked Data
The code under discussion can be found within the `ngsi-ld/store` controller in the
[Git Repository](https://github.com/FIWARE/tutorials.Step-by-Step/blob/master/context-provider/controllers/ngsi-ld/store.js)
### Initializing the library
As usual, the code for HTTP access can be split out from the business logic of the Supermarket application itself. The
lower level calls have been placed into a library file, which simplifies the codebase. This needs to be included in the
header of the file as shown. Some constants are also required - for the Supermarket data, the `LinkHeader` is used to
define location of the data models JSON-LD context as
`https://fiware.github.io/tutorials.Step-by-Step/tutorials-context.jsonld`.
```javascript
const ngsiLD = require('../../lib/ngsi-ld');
const LinkHeader =
'; rel="http://www.w3.org/ns/json-ld#context"; type="application/ld+json">';
```
### Retrieve a known Store
This example reads the context data of a given **Store** entity to display the results on screen. Reading entity data
can be done using the `ngsiLD.readEntity()` method - this will fill out the URL for the GET request and make the
necessary HTTP call in an asynchronous fashion:
```javascript
async function displayStore(req, res) {
const store = await ngsiLD.readEntity(
req.params.storeId,
{ options: 'keyValues' },
ngsiLD.setHeaders(req.session.access_token, LinkHeader)
);
return res.render('store', { title: store.name, store });
}
```
The function above also sends some standard HTTP Headers as part of the request - these are defined in the
`setHeaders()` function.
Within an NGSI-LD-based system, the usual default HTTP headers would include a `Link` header to send the JSON-LD context
and a `Content-Type` header to identify the request as `application/ld+json` (note that every NGSI-LD request is valid
JSON_LD since NGSI-LD is a subset of JSON-LD). Other additional headers such as `X-Auth-Token` can be added to enable
OAuth2 security.
```javascript
function setHeaders(accessToken, link, contentType) {
const headers = {};
if (accessToken) {
headers['X-Auth-Token'] = accessToken;
}
if (link) {
headers.Link = link;
}
if (contentType) {
headers['Content-Type'] = contentType || 'application/ld+json';
}
return headers;
}
```
Within the `lib/ngsi-ld.js` library file, the `BASE_PATH` defines the location of the Orion Context Broker, reading a
data entity is simply a wrapper around an asynchronous HTTP GET request passing the appropriate headers
```javascript
const BASE_PATH = process.env.CONTEXT_BROKER || 'http://localhost:1026/ngsi-ld/v1';
function readEntity(entityId, opts, headers = {}) {
return request({
qs: opts,
url: BASE_PATH + '/entities/' + entityId,
method: 'GET',
headers,
json: true
});
}
```
The equivalent cUrl statement can be seen below:
```console
curl -G -X GET 'http://localhost:1026/ngsi-ld/v1/entities/urn:ngsi-ld:Building:store001/' \
-H 'Link: ; rel="http://www.w3.org/ns/json-ld#context"; type="application/ld+json"' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d 'options=keyValues'
```
## Aggregating and Traversing Linked Data
To display information at the till, it is necessary to discover information about the products found within a Store.
From the Data Entity diagram we can ascertain that:
- **Building** entities hold related **Shelf** information within the `furniture` _Relationship_
- **Shelf** entities hold related **Product** information within the `stocks` _Relationship_
- Products hold `name` and `price` as _Property_ attributes of the **Product** entity itself.
Therefore the code for the `displayTillInfo()` method will consist of the following steps.
1. Make a request to the Context Broker to _find shelves within a known store_
2. Reduce the result to a `id` parameter and make a second request to the Context Broker to _retrieve stocked products
from shelves_
3. Reduce the result to a `id` parameter and make a third request to the Context Broker to _retrieve product details
for selected shelves_
To users familiar with database joins, it may seem strange being forced to making a series of requests like this,
however it is necessary due to scalability issues/concerns in a large distributed setup. Direct join requests are not
possible with NGSI-LD.
### Find Shelves within a known Store
To access the `furniture` attribute of a known **Building** entity, a `keyValues` request is made using the `attrs`
parameter.
```javascript
const building = await ngsiLD.readEntity(
req.params.storeId,
{
options: 'keyValues',
attrs: 'furniture'
},
ngsiLD.setHeaders(req.session.access_token, LinkHeader)
);
```
The equivalent cUrl statement can be seen below:
```console
curl -G -X GET 'http://localhost:1026/ngsi-ld/v1/entities/urn:ngsi-ld:Building:store001/' \
-H 'Link: ; rel="http://www.w3.org/ns/json-ld#context"; type="application/ld+json"' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d 'options=keyValues ... ...
近期下载者:
相关文件:
收藏者: